Modeling behaviors student&teacher
From Santa Fe Institute Events Wiki
Introduction
Background
- Impact of Teacher’s Qualification and Effort on Students’ Performance
In the project, we study the impact of teacher's quality (in term of qualification (proxy by salary), and sets of activities s/he organizes) on minority/marginalized students. Under Chinese elite educational system, there is a large group of marginalized high school students who have been ignored due to the emphasis on exam-oriented results. As a result, teachers have primarily paid more attention to good students since number of good students produced by a teacher is used as a promotion marker which is in turn used as a salary increase index. This practice has unattended consequences on various socio-economic factors, drop-out rates and crime rates.
Objectives
The study was motivated by previous empirical investigations on two secondary vocational schools in China. From this study, it was observed that teachers’ attitudes and behaviors (proxy for various activities they organized) are significant factors that motivate these students to tuned down their personalities and behaviors (note: these students are troubled students). It was thus recommended that improvement of students’ personality and behaviors should served as the prime index in teacher’s salary. Only in this matter can teachers be motivated to devote ample of time in exploring various educational methods on these students. According to the previous research and data analysis from the questionnaires, we will model the bidirectional interactions between students and teachers in NetLogo to investigate some of the assumptions made in the above statements.
Members
Modeling
Model Thoughts
- Current situation:
Graduation rate is one of the critical index in teacher’s salary. Teachers don’t concern inferior students. Thus the decreasing numbers of these students’ properties have no link to teacher’s salary.
- Suggestion:
Set students’ normalized personality and behaviors as prime index in teacher’s salary. Thus the properties of these students have strong links to teachers’ salary.
- Initial condition of student:
- Four properties: learningSkill, acceptanceToTeacher, normalizedCharacter, normalizedBehavior.
- Every property is decreasing when the model starts.
- Initial condition of teacher:
- One property : Salary.
- Salary equals 1000.
- actions: Encourage sutents.Organize activities
- Condition: make conection between teacher's salary and students' performance or not.We can use switch.
- if switch-off: Student’s properties decrease continually -------- Teacher dose nothing and his salary keeps steadily.
- if switch-on : Every student property is decreasing in every time step.(This is initial condition).If sum of four student properties < a(We can define 'a' in the model), then teacher’s salary starts to subtract 50 in every time step. And If salary < radom s1, (400 < s1 < 600), teacher will take “actions”.
Teacher takes action1——encourage students.
77.83% of students make progress on two properties: learningSkill and acceptanceToTeacher.These two two properties will increase in every step.
Teacher takes action2 ——organize social activies.
53.2% of students change better on two properties: normalizedCharacter+1 and normalizedBehavior.These two two properties will increase in every step.
Teacher takes action1 and action2——encourage students and organize social activies.
- Feedback loop:
If sum of four student properties > b, then teacher’s salary starts to plus 50 in evert time step. If salary>random s2, (1500<s2<2000,s2 is the threshold of salary satisfaction), the contact between teacher and students will be more frequent and their links will be thicker.
Modeling Working
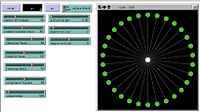
We are thinking to use the structure of small world and model the behaviors between one teacher and 40-60 students.We put one teacher in the center and students around this teacher. Use sliders to control the weight and pramaters and see the changes of links between teacher and students.
In this advanced model, we replace the links with "Dancing Color" to express the interactions between students and teacher.Blue color and larger size mean this student becomes better. Red color and smaller size mean this student becomes worse. Green color means no change.
Data Collecting
- Major variables:
- number-of-student: Total number of students.
- action-weight: Teacher has two actions:Encourage student and Organize activities. This variable is the weight to choose different actions.
- teffort: This is teacher's effort.How hard teaher works. This variable is affected by salary.
- g-rate: The sum of probability to become better of one student.
- b-rate: The sum of probability to become worse of one student.
- per-good: The proportion of good students.
- salary: Teacher's salary.400<salay<2000.
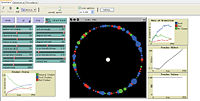
- Experiment 1 : We fix all slighters except number-of-student and action-weight.Number-of-student is from 10 to 190 and the increment is 20. Action-weight is from 0 to 1 and increment is 0.2.And analyze the relationship between two unfixed varibales and per-good, teffort, g-rate,b-rate respectively. From the observation of diagrams, we find we need to focus on some particular ranges.
- Experiment 2: Number-of-student is from 90 to 110 and the increment is 5. Action-weight is from 0 to 1 and increment is 0.2. The measured value is teffort.
- Experiment 3: Number-of-student is from 95 to 100 and the increment is 1. Action-weight equals 0.4.The measured value is teffort.
- Experiment 4: Number-of-student is from 30 to 110 and the increment is 5. Action-weight is from 0 to 1 and increment is 0.2. The measured value is b-rate.
- Experiment 5: Number-of-student is from 10 to 200 and the increment is 100. Action-weight equals 0.4.The measured value is salary.
Original Discussion
Chang Yu:I’m doing some research about a marginalized group of high school students under Chinese elite education policy. These students can’t handle the exam-oriented school circumstance and get ignored and even discriminated. Some of them have character defect. From the six-month field research and data analysis, I find teachers’ attitudes and behaviors are the most significant factors when children grow up. Now I hope to use NetLogo to model the bidirectional behaviors between students and teachers.
Here are some draft ideas I’m thinking about:
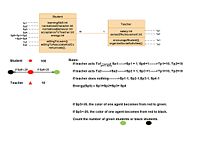
- Student’s properties: learning skill (Sp1), normalized character (Sp2), normalized behavior(Sp3) ,acceptance to teacher (Sp4)
- Student’s actions: be willing to learn (Sa1), be willing to associate and communicate (Sa2)
- Teacher’s properties: salary (Tp1), sense of achievement (Tp2)
- Teacher’s actions: encourage students (Ta1), organize social activities (Ta2)
- Rules: (I’m still thinking)
- If teacher acts Ta1----> Sa1----> Sp1 + 1, Sp4+1----> Tp1+1, Tp2+1
- If teacher acts Ta2----> Sa2----> Sp2 + 1, Sp3 +1---> Tp1+1, Tp2+1
(Also have the negative rules and combination rules, like Ta1+Ta2--->Sa2----> Sp2 + 1, Sp3 +1)
SOS!! If you guys have any ideas, suggestions, help about NetLogo, please please please tell me !
Alhaji Cherif:Interesting idea, you might want to take a look at the following working papers (they are mathematical (math. epidemiology) in nature):
Katie Diazrlene, Cassie Fett, Griselle Torres-Garcia, Nicolas M. Crisosto (2003) The Effects of Student-Teacher Ratio and Interactions on Student/Teacher Performance in High School Scenarios. MTBI BU-1645-M
Abstract: We develop a model that incorporates the impact of sudden-teacher ratio on the performance dynamics of both teachers and students. The model assumes that the members of both populations may be found in three dynamics states: positive, discouraged and reluctant. The role of complex nonlinear interactions between students and teachers, as well as the role of recruitment and intervention, are studied via analytic and numerical studies. Using center manifold theory we find conditions for the existence of a backward bifurcation that support endemic stationary states below the critical threshold value, R0 < 1, when normally only a positive environment would be supported. Our simulations show that in order to maintain a positive environment for students and teachers, R0 must be reduced significantly. Since R0 is a function of student-teacher ratio this can be achieved by decreasing class size.
Corvina Boyd, Alison Castro, Nicolas M. Crisosto, Arlene Evangelista, Christogher Kribs-Zaleta, Carlos Castillo-Chávez (2000) A Socially Transmitted Disease: Teacher Qualifications and High School Drop-Out Rates MTBI BU-1526-M
Abstract The main goal of this study is to quantify the impact of teacher interactions on student achievement to facilitate recommending policy strategies that minimize high school dropout rates. This study derives a system of differential equations that examine the effects that teachers have on minority high school students' learning experience in California and Arizona. The first mathematical model focuses on the impact that teacher dynamics have on a school's faculty composition. Teacher's dynamics are coupled with a second system that models student responses to teacher preparation and experience in order to investigate the effects of these interactions on high school dropout and completion rates.
If you cannot locate the paper online, let me know, I know some of the authors of the two papers.
Chang Yu:Thank u Alhaji! I really appreciate if you could tell me how to get the papers. Have you done any research in this area? We should talk about it! Thanks.
Chang Yu:I think this picture could be a better way to explain this project.
Original Data
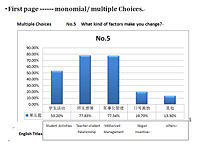
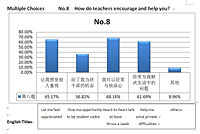
This research in China includes questionnaire survey for 200 students. The questionnaire has two pages. First page is monomial/ multiple Choices and second page is scale-measure topics. We use Frequency Analysis, Tests of Between-Subjects Effects and Multiple Linear Regression Analysis. I translate these questions and data analysis which are related with teachers.