Information Theory of the Heart Page
From Santa Fe Institute Events Wiki
Contact: Hiroshi (hashika1@jhmi.edu)
Thank you for your interest in the project. Feel free to join us any time and share your thoughts!
06/12/2014(Thu) Brainstorming Session
Why: To identify adaptive mechanisms leading to cardiac arrhythmia in diseased hearts. Then localize the origin of arrhythmia (= wavebreak) and treat it before it happens.
Hypothesis: Arrhythmias result from an adaptive mechanism to optimize information transmission in abnormal hearts.
Challenge: Wavebreaks can also occur in normal heart tissue. Would information theory metrics be sensitive enough?
How: Time series from a cellular automata model of the 2-D heart tissue. ?Time series of invasive electrogram from animal or human
What: To quantify information transmission within the heart
Potential Metrics
Mutual information of binary time series (0–resting, 1–excited) in two locations. A high mutual information suggests electrical coupling.
Permutation Entropy - Temporal uncertainty in one location. Time series in rational numbers.
Transfer Entropy - Spatial uncertainty between two locations. Time series in binary numbers.
06/13/2014(Fri) Unofficial Brainstorming Session
Thank you all for suggesting excellent reference articles.
1. Cao et al., Detecting Dynamical Changes in Time Series Using the Permutation Entropy. File:2004 CaoY PRE.pdf - Application of Permutation Entropy to EEG data
2. Rosso et al., Distinguishing Noise from Chaos. File:2007 RossoOA PRL.pdf - Complexity–Entropy Causality plane
3. Lacasa et al., From Time Series to Complex Networks: The Visibility Graph. File:2008 LacasaL PNAS.pdf
4. Lizier et al., Local Information Transfer as a Spatiotemporal Filter for Complex Systems. File:2008 LizierJT PRL.pdf - Local Transfer Entropy
5. Cheong et al., Information Transduction Capacity of Noisy Biochemical Signaling Networks. File:2011 Cheong Science.pdf - Not quite relevance but important for future applications.
Let's read the reference papers above this weekend and discuss what exactly we should measure at the next meeting. The next meeting will be at 02:30pm on Monday 06/16/2014 (after my tutorial[1]) in the lecture hall. If you have any questions I will be around this weekend. You will most certainly find me in the common room (or wherever TV is available) at 7pm on Saturday 06/14/2014 for FIFA World Cup Japan vs. Côte d'Ivoire!
06/15/2014(Sun) Group Meeting
Meeting with Josh @11:00am to discuss the project. Location: ARIEL
 .
.
Thank you everyone for great discussions!
Summary of Information Theory Indices to Quantify Information Transfer within the Heart
Question: So which one would help identify the location of wavebreaks (= intersection between wavefront and wavetail)?
1. Mutual Information 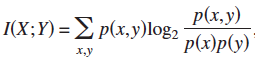 ;
; ![]()
2. Conditional Mutual Information ![]()
3. Transfer Entropy (from state Y to X) 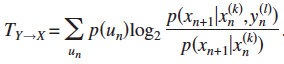 ;
; ![]()
= Conditional Mutual Information regarding the next state X' ![]()
= Global average of a Local Transfer Entropy at each observation ![]()
4. Local Transfer Entropy 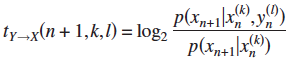 ; Binary time series.
; Binary time series.
See Lizier File:2008 LizierJT PRL.pdf and his recent book chapter[2]
5. Permutation Entropy ![]() where the sum runs over all n! permutations pi of order n. Real-value time series.
where the sum runs over all n! permutations pi of order n. Real-value time series.
See Bandt and Pompe File:2002 Bandt PRE.pdf and Cao File:2004 CaoY PRE.pdf
6. Complexity-Entropy Causality Plane. See Rosso File:2007 RossoOA PRL.pdf
7. Visibility Graph: A simple rule to map real-valued time series into a network. See Lacasa File:2008 LacasaL PNAS.pdf
8. Graph Entropy: Quantifies structural information of a graph based on a derived probability distribution. See Dehmer File:2008 Dehmer AMC.pdf
Project Milestones
1. Build a 2-D cellular automata model of realistic heart tissue (Matlab)
Available Resources: Netlogo codeFile:Example.nlogo; Original code is here[3]
