Information Theory of the Heart Page
From Santa Fe Institute Events Wiki
Contact: Hiroshi (hashika1@jhmi.edu)
Thank you for your interest in the project. Feel free to join us any time and share your thoughts!
06/12/2014(Thu) Brainstorming Session
Why: To identify adaptive mechanisms leading to cardiac arrhythmia in diseased hearts. Then localize the origin of arrhythmia (= wavebreak) and treat it before it happens.
Hypothesis: Arrhythmias result from an adaptive mechanism to optimize information transmission in abnormal hearts.
Challenge: Wavebreaks can also occur in normal heart tissue. Would information theory metrics be sensitive enough?
How: Time series from a cellular automata model of the 2-D heart tissue. ?Time series of invasive electrogram from animal or human
What: To quantify information transmission within the heart
Potential Metrics
Mutual information of binary time series (0–resting, 1–excited) in two locations. A high mutual information suggests electrical coupling.
Permutation Entropy - Temporal uncertainty in one location. Time series in rational numbers.
Transfer Entropy - Spatial uncertainty between two locations. Time series in binary numbers.
06/13/2014(Fri) Unofficial Brainstorming Session
Thank you all for suggesting excellent reference articles.
1. Cao et al., Detecting Dynamical Changes in Time Series Using the Permutation Entropy. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 70: 046217, 2004 File:2004 CaoY PRE.pdf
2. Rosso et al., Distinguishing Noise from Chaos. Phys Rev Lett 99: 154102, 2007 File:2007 RossoOA PRL.pdf
3. Lacasa et al., From Time Series to Complex Networks: The Visibility Graph. PNAS 105: 4972, 2008 File:2008 LacasaL PNAS.pdf
4. Lizier et al., Local Information Transfer as a Spatiotemporal Filter for Complex Systems. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 77: 026110, 2008 File:2008 LizierJT PRL.pdf
5. Cheong et al., Information Transduction Capacity of Noisy Biochemical Signaling Networks. Science 334: 354, 2011 File:2011 Cheong Science.pdf
Let's read the reference papers above this weekend and discuss what exactly we should measure at the next meeting. The next meeting will be at 02:30pm on Monday 06/16/2014 (after my tutorial[1]) in the lecture hall. If you have any questions I will be around this weekend. You will most certainly find me in the common room (or wherever TV is available) at 7pm on Saturday 06/14/2014 for FIFA World Cup Japan vs. Côte d'Ivoire!
06/15/2014(Sun) Group Meeting
Meeting with Josh @11:00am to discuss the project. Location: ARIEL
 .
.
Thank you everyone for great discussions!
Summary of Information Theory Indices to Quantify Information Transfer within the Heart
Question: So which one would help identify the location of wavebreaks (= intersection between wavefront and wavetail)?
1. Mutual Information 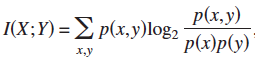 ;
; ![]()
2. Conditional Mutual Information ![]()
3. Transfer Entropy (from state Y to X) 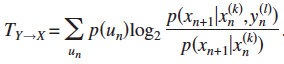 ;
; ![]()
= Conditional Mutual Information regarding the next state X' ![]()
= Global average of a Local Transfer Entropy at each observation ![]()
4. Local Transfer Entropy 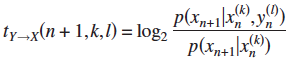 ; Binary time series.
; Binary time series.
See Lizier et al., 2008 File:2008 LizierJT PRL.pdf and his recent book chapter[2]
5. Permutation Entropy ![]() where the sum runs over all n! permutations pi of order n. Real-value time series.
where the sum runs over all n! permutations pi of order n. Real-value time series.
See Bandt and Pompe, 2002 File:2002 Bandt PRE.pdf and Cao et al., 2004 File:2004 CaoY PRE.pdf
6. Complexity-Entropy Causality Plane. See Rosso et al., 2007 File:2007 RossoOA PRL.pdf
7. Visibility Graph: A simple rule to map real-valued time series into a network. See Lacasa et al., 2008 File:2008 LacasaL PNAS.pdf
8. Graph Entropy: Quantifies structural information of a graph based on a derived probability distribution. See Dehmer, 2008 File:2008 Dehmer AMC.pdf
